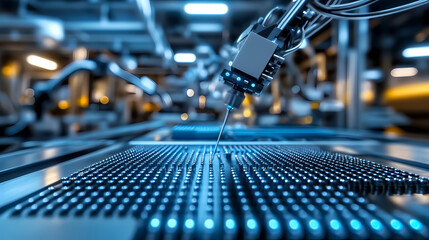
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are integral to the functioning of nearly all electronic devices. PCB manufacturing involves the creation of a conductive pathway on a non-conductive base material, allowing electrical components to interact and function. Without PCBs, electronic devices like smartphones, televisions, and computers would be unable to operate. As the demand for compact, multi-functional devices grows, PCB manufacturing plays a crucial role in enabling increasingly complex and efficient electronics.
PCB Design: The Foundation of Manufacturing
The process of PCB Manufacturing begins with meticulous design. Engineers use specialized software to map out the circuit pathways, component placement, and electrical specifications required for the board’s functionality. The design process ensures that the PCB will work as intended when it is produced, considering factors like signal integrity, thermal management, and component spacing. Proper PCB design is essential for creating reliable and efficient electronic products that meet the consumer’s high expectations.
Materials Used in PCB Manufacturing
Choosing the right materials is fundamental to PCB manufacturing. The substrate, typically made from materials like fiberglass or composite epoxy, provides the foundation for the circuit board. Conductive materials, usually copper, form the pathways that transmit electrical signals across the PCB. Additionally, various layers of insulating materials, solder masks, and silkscreen layers are applied to protect the components and ensure durability. The choice of materials greatly influences the performance and longevity of the PCB, ensuring that electronic devices are reliable and functional.
The Rise of Flexible PCBs
As technology advances, one of the significant trends in PCB manufacturing is the rise of flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs). These boards are highly versatile and can be bent or twisted to fit into compact and unique spaces, making them perfect for wearable devices, medical implants, and automotive applications. FPCBs enable the creation of lighter, smaller, and more durable electronic devices, which have opened up new possibilities for innovation. The flexibility they offer is changing the way manufacturers think about the design and functionality of their products.
The Step-by-Step Process of PCB Manufacturing
PCB manufacturing involves several key steps to ensure the final product meets the required standards. The process begins with material preparation, followed by printing the circuit design onto the copper layer using a photolithography process. The boards are then etched, and unwanted copper is removed to form the desired circuit pattern. Afterward, the board is drilled, and holes are created for mounting components. The final steps include applying a solder mask, adding a silkscreen for identification, and testing the board to ensure it meets electrical standards.
Emerging PCB Technologies
In addition to flexible PCBs, other emerging PCB technologies are shaping the future of electronics. High-frequency PCBs, for example, are designed to handle signals at microwave and radio frequencies, which are essential in applications like telecommunications and radar systems. The advent of 3D printing in PCB manufacturing has also opened new doors for creating more intricate and complex designs. These technologies will continue to evolve, allowing manufacturers to meet the increasing demands for more powerful, efficient, and miniaturized electronic devices.
Environmental Impact of PCB Manufacturing
As the electronics industry grows, so does the environmental impact of PCB manufacturing. The production process involves chemicals and materials that can be hazardous if not properly handled. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting environmentally friendly practices, such as using lead-free solder and reducing the use of harmful chemicals. Additionally, the push for recyclability and sustainability is shaping the future of PCB manufacturing. As industries seek to minimize their environmental footprint, sustainable practices will become more widespread in PCB production.
The Global PCB Manufacturing Landscape
The global demand for PCBs has been growing steadily, driven by the rise of new technologies like 5G, electric vehicles, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Asia-Pacific remains the largest region for PCB manufacturing, with China, Japan, and South Korea being major players. However, the industry is witnessing a shift towards more localized manufacturing, with the emergence of new markets in North America and Europe. The changing global landscape reflects the growing importance of PCBs across various industries, prompting manufacturers to adapt and stay competitive.
Conclusion
PCB manufacturing is essential for the development of reliable, high-performance electronic devices. As consumer demand grows for smarter, smaller, and more capable electronics, the role of PCB manufacturing becomes even more crucial. From the design phase to advanced technologies and the challenges faced by manufacturers, the process continues to evolve. By embracing innovation and ensuring precision at every step, the PCB manufacturing industry will remain vital in shaping the future of electronics, driving technological advancement in numerous sectors.